Variable transformations
Variable transformations have many purposes. For example, they may help you normalize your data. Do it in Excel using the XLSTAT statistical software.
Use of variable transformation
Variable transformation is often necessary to get a more representative variable for the purpose of the analysis. It can also be used simply to let your variable's distribution get closer to a normal distribution (notice that this does not work systematically).
Deciding on the appropriate transformation will often improve the quality of your results.
XLSTAT variable transformation functions
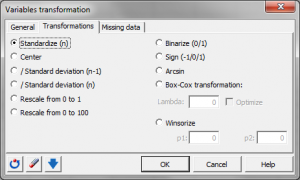
This function allows you to transform a quantitative variable using many different analytical functions.
XLSTAT provides the following analytical functions:
- Standardize (n-1) To standardize the variables using the unbiased standard deviation.
- Standardize (n) To standardize the variables using the biased standard deviation.
- Center To center the variables.
- 1/ Standard deviation (n-1) To divide the variables by their unbiased standard deviation.
- 1/ Standard deviation (n) To divide the variables by their biased standard deviation.
- Rescale from 0 to 100
- Binarize (0/1) To convert all values that are not 0 to 1, and leave the 0s unchanged.
- Sign (-1/0/1) To convert all values that are negative to -1, all positive values to 1, and leave the 0s unchanged.
- Arcsin
- Box-Cox transformation To improve the normality of the sample.
- Winsorize To remove data that are not within an interval defined by two percentiles.
- Johnson transformation To improve the normality of the sample.


analyze your data with xlstat
14-day free trial